
-
 Nefu
Nefu - 22 Dec 2025
- Getting started
How to Transfer Crypto from Exchange to Wallet Safely
Introduction: Why Transfer Crypto to Your Own Wallet After buying cryptocurrency on an exchange, many beginners leave it there for convenience. However, exchanges are frequent targets for hacks, and "not your keys, not your crypto" remains a core principle. Moving your assets to a personal wallet gives you full control and significantly improves security. Searches like "how to transfer crypto from exchange to wallet" and "move bitcoin from coinbase to wallet" are common because this step marks the transition to proper self-custody. This guide explains the complete process safely and clearly for 2026. We cover preparation, step-by-step transfer, fees, common mistakes, and verification tips. Strengthen your knowledge with our best crypto wallets for beginners and review pitfalls in our 10 biggest crypto mistakes. Preparation: Set Up Your Wallet First Never buy crypto before having a wallet ready.Choose and install a reputable wallet (see our recommendations). Complete setup and securely back up your seed phrase offline. Generate a receive address for the specific cryptocurrency you plan to transfer.Popular beginner options:MetaMask or Trust Wallet for multi-chain. Phantom for Solana (see our Phantom setup tutorial). Hardware wallets like Ledger for larger amounts.Step-by-Step: Transferring Crypto from Exchange to Wallet The process is similar across platforms like Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Crypto.com. Step 1: Log In to Your Exchange Account Use official apps or websites and ensure 2FA is enabled. Step 2: Navigate to Withdrawals Find "Withdraw," "Send," or "Wallet → Withdraw" section. Step 3: Select the Cryptocurrency Choose the exact asset (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, USDT). Pay attention to network selection for tokens. Step 4: Paste Your Wallet Receive Address Copy the address from your personal wallet and paste it carefully.Critical: Double-check the first and last 6 characters. Use copy-paste — never type manually. For tokens like USDT or USDC:Match the network exactly (e.g., ERC-20, TRC-20, Solana). Mismatched networks can result in permanent loss.Step 5: Enter Amount Input how much to send. Leave enough for fees if required. Step 6: Review Fees and Limits Exchanges charge:Withdrawal fee (fixed or percentage). Network fee (miner/validator cost, varies by congestion).Bitcoin fees can spike during busy periods; Ethereum layer-2 options are cheaper. Step 7: Complete Security Checks Confirm via email, 2FA, or whitelist verification if enabled. Step 8: Submit and Wait Most transfers complete in minutes to an hour, depending on the blockchain. Step 9: Verify Receipt Check your personal wallet balance and use a blockchain explorer for confirmation. Test Transaction First Always send a small amount ($10-50 equivalent) first:Complete full transfer process with minimal value. Confirm arrival and correct address. Send the remainder once verified.This prevents catastrophic loss from address errors. Common Networks and ExamplesCrypto Common Networks NotesBitcoin Native Bitcoin Only one optionEthereum Ethereum (ERC-20), Arbitrum, Optimism Choose cheaper layer-2 when possibleUSDT/USDC ERC-20, TRC-20, Solana, Polygon Match exactly or funds are lostSolana Solana Very low fees, fastBNB BEP-20 (BNB Chain) Low cost alternativeCommon Mistakes and How to Avoid ThemWrong AddressSolution: Always copy-paste and verify ends.Network MismatchSolution: Confirm sender and receiver support the same chain.Missing Memo/TagFor exchanges like Binance or Ripple (XRP), some require a destination tag.Solution: Include if prompted.Insufficient FeesSolution: Most platforms handle this automatically.Sending to Wrong Wallet TypeSolution: Ensure your wallet supports the asset and network.See our full list in the biggest crypto mistakes guide. Fees Overview in 2026Asset Typical Withdrawal Fee (Exchange) Network Fee RangeBitcoin $1-10 $1-50 (congestion)Ethereum $1-5 (mainnet) $0.50-20Solana <$0.01 <$0.01Stablecoins $1-5 Varies by networkLayer-2 solutions and chains like Solana keep costs minimal. Advanced Security TipsEnable withdrawal address whitelisting on exchanges (only pre-approved addresses). Use hardware wallets for signing large transfers. Avoid public Wi-Fi during transactions. Bookmark official sites to prevent phishing.After Transfer: What Next?Hold long-term with proper backups. Use dollar-cost averaging for additional purchases. Monitor portfolio sparingly to avoid emotional stress — see our crypto psychology guide.Conclusion: Take Control of Your Assets Transferring crypto from exchange to wallet is a crucial step toward true ownership and security. The process is simple once understood, but attention to detail is essential. Follow this guide, start with test transactions, and prioritize correct addresses and networks. Self-custody protects your investment far better than leaving funds on platforms. Combine this with safe buying practices from our how to buy Bitcoin guide or general how to buy crypto. You now have the tools for responsible crypto ownership in 2026. Stay vigilant and enjoy the benefits of decentralization.

-
 Nefu
Nefu - 22 Dec 2025
- Getting started
Top 10 Cryptocurrencies Explained for Absolute Beginners
Introduction: The Top 10 Cryptocurrencies Beginners Should Know When I first got started in crypto there were only a few choices to choose from, you had Bitcon, Eth, Xrp, bitcoin cash, litecoin, and dogecoin. Times have changed many of those are still in the top, but we never had so many choices for altcoins back then, and many have the technology to be in the top 10 one day, but for now these are the coins that are at the top currently. The cryptocurrency market includes thousands of projects, but a small handful dominate in terms of market value, adoption, and influence. The top 10 cryptocurrencies represent the vast majority of the total market capitalization. For absolute beginners, focusing on these established coins provides a safer and simpler starting point. Searches like "top cryptocurrencies for beginners" and "best crypto to know 2026" highlight the need for clear, hype-free explanations. This guide covers the top 10 cryptocurrencies (based on consistent rankings over recent years), because each entry explains what the project is, its main purpose, and why it matters without price predictions or investment advice. I'll leave it up to you to decide which one you want to hold in your wallet just use this guide to educate yourself on the top 10. Pair this with our crypto terminology glossary for definitions and our detailed comparison in Bitcoin vs Ethereum for beginners. 1. Bitcoin (BTC) The original cryptocurrency, launched in 2009. What it is: Digital money designed to work without banks or governments.Main purpose: Store of value (often called digital gold) and medium of exchange.Key feature: Fixed supply of 21 million coins.Why it matters: Highest adoption, strongest security, and institutional recognition. 2. Ethereum (ETH) The leading programmable blockchain, launched in 2015. What it is: A platform for building decentralized applications and smart contracts.Main purpose: Power DeFi, NFTs, gaming, and Web3 services.Key feature: Transitioned to energy-efficient Proof of Stake.Why it matters: Hosts the majority of innovative crypto projects. 3. Tether (USDT) The most widely used stablecoin. What it is: A cryptocurrency pegged 1:1 to the US dollar.Main purpose: Provide stability for trading and transfers without converting to fiat.Key feature: Backed by reserves (cash and equivalents).Why it matters: Highest trading volume; essential for moving value across exchanges. 4. Binance Coin (BNB) Native token of the Binance ecosystem. What it is: Utility token for the world's largest exchange and its blockchain (BNB Chain).Main purpose: Pay reduced trading fees and power decentralized apps on BNB Chain.Key feature: Regular token burns reduce supply.Why it matters: Deep integration with one of the biggest trading platforms. 5. Solana (SOL) High-performance blockchain launched in 2020. What it is: A fast, low-cost layer-1 network.Main purpose: Support high-throughput applications like DeFi, NFTs, and gaming.Key feature: Capable of thousands of transactions per second at very low fees.Why it matters: Popular alternative to Ethereum for cost-conscious developers and users.6. USD Coin (USDC) Another major stablecoin, issued by Circle. What it is: Fully reserved US dollar-backed digital currency.Main purpose: Stable trading and payments with transparent audits.Key feature: Regulated issuer and monthly reserve attestations.Why it matters: Trusted by institutions and widely integrated. 7. XRP (Ripple) Token associated with the Ripple payment protocol. What it is: Digital asset designed for fast cross-border payments.Main purpose: Enable quick, cheap international transfers for banks and payment providers.Key feature: Transactions settle in seconds.Why it matters: Strong focus on real-world financial institution partnerships. 8. Cardano (ADA) Research-driven blockchain launched in 2017. What it is: Proof of Stake platform emphasizing academic rigor and sustainability.Main purpose: Support decentralized applications with strong governance.Key feature: Peer-reviewed development approach.Why it matters: Growing ecosystem in Africa and focus on long-term scalability. 9. Dogecoin (DOGE) Originally created as a meme coin in 2013. What it is: Community-driven cryptocurrency based on the Shiba Inu dog meme.Main purpose: Tipping, charitable donations, and light-hearted payments.Key feature: Unlimited supply and strong social media presence.Why it matters: Demonstrates the power of community and viral adoption. 10. TRON (TRX) Blockchain focused on content and entertainment. What it is: Platform for decentralized content sharing and dApps.Main purpose: Reduce intermediary costs for creators and support stablecoin transfers.Key feature: High throughput and low fees.Why it matters: Large user base in entertainment and stablecoin activity. Quick Comparison TableRank Coin Type Main Use Case Supply Model1 Bitcoin Currency Store of value Fixed (21M)2 Ethereum Platform Smart contracts & dApps Inflationary3 Tether Stablecoin Trading stability Pegged to USD4 BNB Utility token Exchange fees & ecosystem Deflationary burns5 Solana Layer-1 blockchain High-speed applications Inflationary6 USDC Stablecoin Regulated stability Pegged to USD7 XRP Payment token Cross-border transfers Fixed8 Cardano Platform Research-driven dApps Inflationary9 Dogecoin Meme coin Community & tipping Unlimited10 TRON Content platform Entertainment & stablecoins InflationaryWhat Beginners Should Focus On Most of the top 10 fall into three categories:Core Assets (Bitcoin, Ethereum): Best for learning fundamentals. Stablecoins (USDT, USDC): Essential for trading and preserving value. Established Altcoins (Solana, BNB, etc.): Offer exposure to different ecosystems.Start with Bitcoin and Ethereum for simplicity, then explore stablecoins when trading. Where to Learn More or Get StartedCompare Bitcoin and Ethereum in depth: Bitcoin vs Ethereum guide Choose a secure platform: Best crypto exchanges for beginners Follow safe buying steps: How to buy crypto or with credit card/PayPal Store safely: Best crypto wallets recommendationsConclusion: Keep It Simple at First The cryptocurrency space evolves quickly, but these top 10 projects have demonstrated staying power. Understanding them gives you a solid overview of the entire market. Now just cause a coin makes it to the top 10 doesn't mean its going to be there next cycle at the top so dyor. Avoid chasing new or trending coins until you are comfortable with these foundations. Focus on learning, security, and gradual exposure. Study the patterns and learn as much as you can about the team and the direction the coin is going in before you ape in. Refer back to this list as rankings shift slightly over time. Combined with our other beginner resources, you now have a clear map of the most important cryptocurrencies.

-
 Nefu
Nefu - 22 Dec 2025
- Getting started
What is Cryptocurrency? A Complete Beginner's Guide to Blockchain
Introduction: Understanding Cryptocurrency in 2026 Cryptocurrency has moved from the fringes of finance to a mainstream topic discussed in boardrooms, governments, and households worldwide. Terms like Bitcoin, blockchain, and digital assets appear in daily news, yet many people still wonder about the fundamentals. Searches for "what is cryptocurrency" and "blockchain explained for beginners" remain among the most common entry points for newcomers. This guide addresses those questions directly and clearly. By the end of this article, you will understand what cryptocurrency actually is, how the underlying blockchain technology functions, why it represents a significant shift from traditional money, and where it stands in 2026. No technical background is required. Once you grasp these concepts, practical steps become much clearer. Explore our crypto terminology glossary for definitions of key terms used here, or review common pitfalls in our guide to the 10 biggest crypto mistakes beginners make. What Exactly Is Cryptocurrency? Cryptocurrency is digital or virtual money secured by cryptography, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments, most cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology. The first and most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin introduced the idea of peer-to-peer electronic cash that requires no bank or central authority. Today, thousands of cryptocurrencies exist, each with different features and purposes. Some, like Bitcoin, focus on being a store of value. Others, like Ethereum, enable programmable contracts and applications. Key characteristics of cryptocurrency include:Decentralization: Control is distributed across a network of computers rather than a single entity. Transparency: Transactions are recorded publicly on the blockchain, visible to anyone. Immutability: Once confirmed, records cannot be altered. Security: Cryptography protects funds and verifies transactions. Borderless Nature: Transfers can occur globally without intermediaries.These traits make cryptocurrency distinct from conventional fiat money like dollars or euros. How Does Blockchain Technology Work? At the heart of most cryptocurrencies lies blockchain, a revolutionary way to record information. Imagine a shared digital ledger that everyone in a network can view and contribute to, but no single party controls. Each page in this ledger is a "block" containing a list of transactions. Once a block is full and verified, it is linked to the previous block using cryptographic hashes, forming a chain. This structure ensures that altering any block would require changing all subsequent blocks across the entire network, which is computationally impractical. The Process Step by StepTransaction Initiation: Someone sends cryptocurrency to another address. Broadcast: The transaction is transmitted to the network. Validation: Network participants (nodes) check if the transaction follows rules (valid signature, sufficient balance). Block Creation: Valid transactions are grouped into a block. Consensus: Nodes agree on the block using mechanisms like Proof of Work (Bitcoin) or Proof of Stake (many newer networks). Addition to Chain: The block is appended, and participants update their copies. Confirmation: The transaction is considered secure after several subsequent blocks.This decentralized consensus replaces the need for trusted intermediaries like banks. Consensus Mechanisms ExplainedProof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin. Participants compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The winner adds the block and earns rewards. Energy-intensive but highly secure. Proof of Stake (PoS): Used by Ethereum since 2022. Validators are chosen based on staked coins. More energy-efficient.Many networks in 2026 use PoS or hybrid models to address environmental concerns. Why Cryptocurrency Matters in 2026 More than fifteen years after Bitcoin's launch, cryptocurrency has achieved significant milestones:Institutional adoption by major companies and investment funds. Regulatory frameworks emerging in many countries. Integration into payment systems and financial products. Growth of decentralized finance offering alternatives to traditional banking.Cryptocurrency addresses real-world issues:Financial inclusion for unbanked populations. Faster and cheaper cross-border transfers. Protection against inflation in unstable economies. Programmable money enabling new applications.However, challenges---
-
 Nefu
Nefu - 21 Dec 2025
- Getting started
Bitcoin 4-Year Cycle Explained for Beginners: Halvings, Bull Runs, Bear Markets, and Altcoins
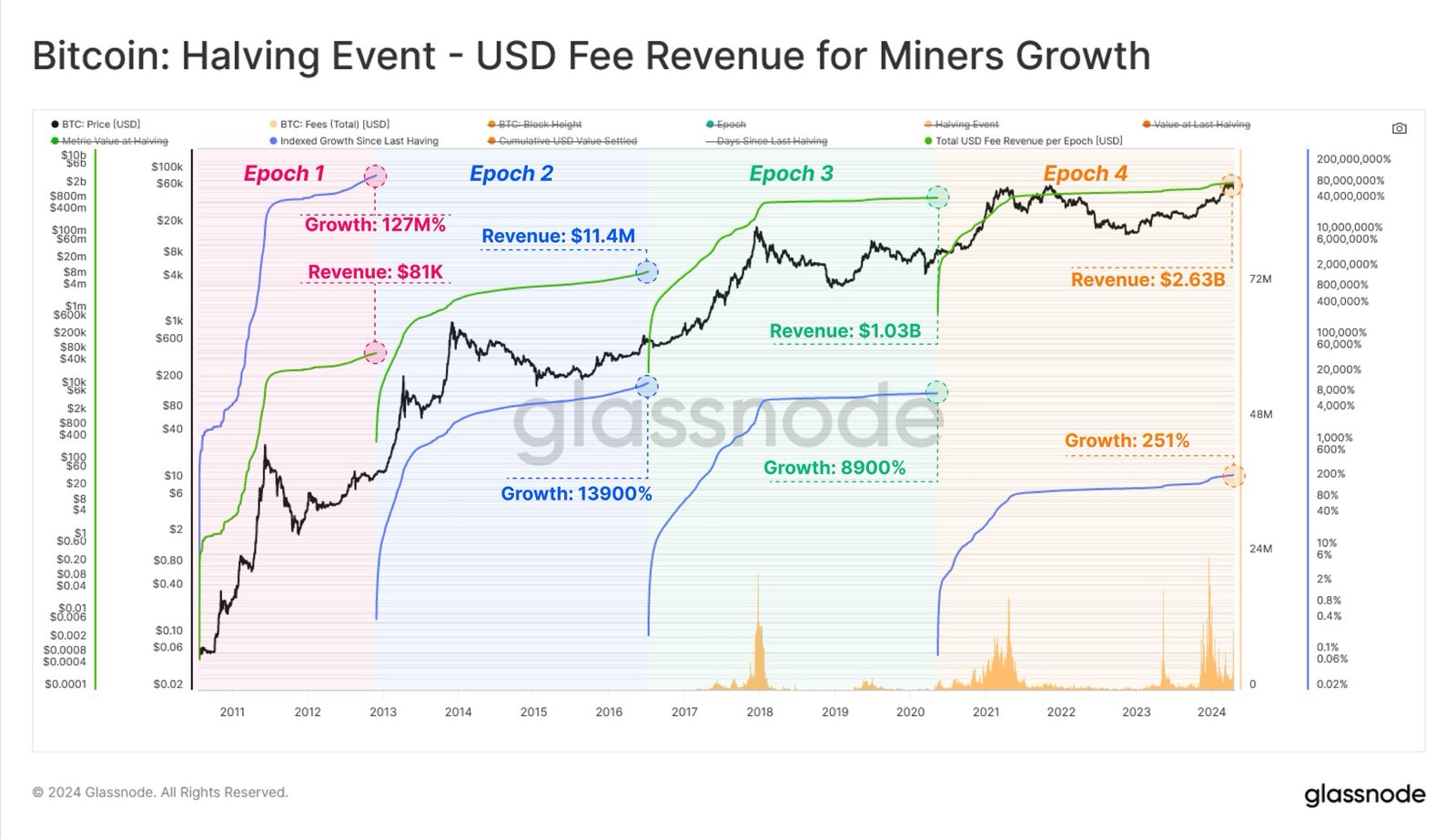
I don't know if anyone has ever told you this but Bitcoin's price doesn't move randomly it's influenced by predictable patterns tied to its core mechanics. The "Bitcoin 4-year cycle" refers to the recurring bull and bear markets roughly every four years, primarily driven by the halving event. For beginners, understanding this cycle is crucial for managing expectations, avoiding panic sells, and timing entries wisely. In this guide, I'll break down the halving mechanism, the typical cycle structure (including the 1066-day bull runs from bear bottoms and 400-day declines from bull tops), historical price evolution from Bitcoin's inception in 2009 to late 2025, and how altcoins often amplify or lag these patterns. This knowledge builds on fundamentals from What is Cryptocurrency? A Complete Beginner's Guide to Blockchain in 2026 and helps prevent the 10 Biggest Crypto Mistakes Beginners Make in 2026, like buying at peaks due to FOMO. By mastering these cycles, you'll align with strategies like Dollar Cost Averaging Explained: The Best Strategy for Crypto Beginners in 2026 and develop the mindset from Crypto Investing Psychology: Mastering Emotions and Avoiding FOMO as a Beginner in 2026. This article serves as an advanced entry in our getting-started pillar, bridging to trading and investing topics. What Is the Bitcoin Halving and Why Does It Matter? The Bitcoin halving is a programmed event every 210,000 blocks (roughly every four years) where the mining reward for new blocks is cut in half. This reduces the rate of new Bitcoin entering circulation, creating a supply shock.How It Works: Bitcoin's total supply is capped at 21 million. Miners receive rewards for validating transactions—starting at 50 BTC per block in 2009, halving to 25 in 2012, 12.5 in 2016, 6.25 in 2020, 3.125 in 2024, and so on until around 2140. Economic Impact: With demand steady or growing, reduced supply often drives prices up over time. Halvings act as catalysts for bull markets.Halvings aren't just technical—they fuel market psychology, sparking speculation and investment inflows.The Structure of Bitcoin's 4-Year Cycle Bitcoin's price history shows repeating cycles aligned with halvings:Bear Market Bottom: After a bull peak, prices crash and consolidate for months, forming a "bottom." Pre-Halving Rally: Anticipation builds, leading to gradual climbs. Post-Halving Bull Run: Explosive growth as supply tightens and adoption surges. Bull Market Top: Euphoria peaks, followed by a sharp correction into the next bear.Historical data reveals patterns:Bull Phase: From bear bottom to bull top, Bitcoin often rises for about 1066 days (roughly 3 years). Bear Phase: From bull top to next bottom, it declines over approximately 400 days (about 13 months).These aren't exact—variations occur due to external factors like regulations, macroeconomics, or events (e.g., 2022's FTX collapse). But the cycle has held across four halvings. Historical Bitcoin Price Cycles: From 2009 to 2025 Bitcoin started at $0 in 2009. Here's a cycle-by-cycle breakdown with approximate prices (log-scale charts show percentage gains clearly). Cycle 1: 2009-2013 (First Halving: November 2012)Bear Bottom: Early 2011 (~$1 after initial hype fade). Bull Run: 1066 days to peak at ~$1,150 in late 2013 (post-halving surge). Bear Decline: 410 days down to ~$200 in early 2015. Key Events: Pizza Day (2010), first exchanges.Cycle 2: 2013-2017 (Second Halving: July 2016)Bear Bottom: January 2015 (~$200). Bull Run: ~1,000 days to all-time high of ~$19,800 in December 2017. Bear Decline: 364 days to ~$3,200 in December 2018. Key Events: Ethereum launch (2015), ICO boom.Cycle 3: 2017-2021 (Third Halving: May 2020)Bear Bottom: December 2018 (~$3,200). Bull Run: ~1,050 days to ~$69,000 in November 2021. Bear Decline: ~370 days to ~$15,500 in November 2022. Key Events: COVID stimulus, institutional adoption (Tesla, MicroStrategy).Cycle 4: 2021-2025 (Fourth Halving: April 2024)Bear Bottom: November 2022 (~$15,500). Bull Run: Projected ~1,066 days, peaking around mid-2025 at over $100,000 (as of December 2025, Bitcoin hovers around $95,000-$105,000 amid ETF inflows). Bear Decline: Expected ~400 days post-peak, bottoming in late 2026. Key Events: Spot ETF approvals (2024), nation-state adoption (El Salvador).From $0 to over $100,000 in 16 years, Bitcoin's compound annual growth rate exceeds 200% in bull phases. How Altcoins Fit Into Bitcoin's Cycles Altcoins (alternative cryptocurrencies like Ethereum, Solana, or memecoins) often follow Bitcoin's lead but with amplified volatility.Correlation: During Bitcoin bull runs, capital flows from BTC to alts ("altseason"), boosting their prices 5-10x more. In bears, alts crash harder (80-95% drops). Timing: Alts lag Bitcoin—rising later in the cycle and bottoming earlier. Examples: In 2017, Ethereum surged 100x during Bitcoin's bull. In 2021, Solana and memecoins like SHIB exploded post-Bitcoin peak. Risks: Altcoins lack Bitcoin's scarcity (no halvings), making them riskier. See Top 10 Cryptocurrencies Explained for Absolute Beginners in 2026 and Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which is Better for Beginners in 2026.Why Cycles Happen: Supply, Demand, and PsychologySupply Shock: Halvings halve inflation, mimicking gold's scarcity. Demand Drivers: Adoption waves (retail, institutions, nations). Psychological Factors: Greed in bulls, fear in bears—cycles reflect human behavior.External influences (e.g., interest rates, geopolitics) can shorten or extend phases. Applying This to Your StrategyBuy Low: Enter near bear bottoms using DCA. Hold Through Volatility: Avoid selling in early bull dips. Diversify to Alts Cautiously: Only after Bitcoin stabilizes. Exit Strategy: Take profits near projected peaks.Secure your holdings first: Use wallets like How to Set Up MetaMask Wallet: Step-by-Step Tutorial for Beginners 2026 or How to Set Up Trust Wallet: Step-by-Step Tutorial for Beginners 2026. Potential Changes in Future Cycles As Bitcoin matures, cycles may diminish (less volatility). The 2028 halving could see softer patterns with mainstream adoption. Final Thoughts Bitcoin's 4-year cycle offers a roadmap for beginners—halvings spark 1066-day bulls from bottoms, followed by 400-day bears. From $0 in 2009 to over $100,000 in 2025, it's a story of growth amid volatility. Altcoins ride the waves but with higher risks. This understanding hubs into advanced trading: Time markets better, avoid emotional traps, and build wealth patiently. Start with How to Buy Bitcoin for Beginners: Complete Step-by-Step Guide 2026 and remember—crypto rewards the informed. Happy cycling!

-
 Nefu
Nefu - 21 Dec 2025
- Getting started
Crypto Terminology Glossary: 100 Essential Terms for Beginners
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Terminology Entering the world of cryptocurrency can feel overwhelming at first. The space is filled with technical jargon, acronyms, and concepts that seem complex on the surface. Terms like blockchain, wallet, mining, and DeFi get thrown around constantly in discussions, news articles, and social media. This glossary is designed specifically for beginners. It covers 100 of the most essential cryptocurrency terms you need to know in 2026. Each definition is explained in straightforward language, with real-world context where helpful. Whether you are researching your first purchase or just trying to follow conversations online, understanding these terms will give you a solid foundation. As the crypto ecosystem evolves rapidly, having a clear grasp of the basics helps you make informed decisions. Once you are familiar with these concepts, you will find it easier to explore topics like choosing an exchange or setting up a wallet. For practical next steps, check out our guide on the best crypto exchanges for beginners or learn how to buy crypto safely. The terms below are organized alphabetically for easy reference. The Glossary: 100 Essential Crypto Terms AddressA unique string of characters that acts as a destination for sending or receiving cryptocurrency, similar to a bank account number but public. AirdropA distribution of free tokens or coins to wallet addresses, often used by projects to promote awareness or reward early users. AltcoinAny cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. Examples include Ethereum, Solana, and Ripple. Bear MarketA prolonged period where prices are falling, leading to pessimistic sentiment among investors. BlockchainA decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers in a secure, immutable way. BlockA collection of transactions grouped together and added to the blockchain after validation. Block RewardThe newly minted coins given to miners or validators as incentive for securing the network. Bull MarketA prolonged period of rising prices and optimistic investor sentiment. Centralized Exchange (CEX)A trading platform operated by a company, such as Coinbase or Binance, that holds user funds. Cold WalletA cryptocurrency storage method offline, like a hardware device, offering high security against hacks. Consensus MechanismThe process networks use to agree on the validity of transactions, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. CryptocurrencyDigital or virtual currency secured by cryptography, operating independently of central banks. Decentralized Application (dApp)An application built on a blockchain that runs without a single controlling entity. Decentralized Exchange (DEX)A peer-to-peer trading platform where users retain control of their funds, like Uniswap. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)Financial services built on blockchain, allowing lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)A strategy of investing fixed amounts regularly, regardless of price, to reduce volatility impact. EthereumThe second-largest blockchain platform, known for smart contracts and decentralized applications. Fiat CurrencyGovernment-issued money, such as USD or EUR, not backed by a physical commodity. ForkA split in a blockchain creating two separate versions, either hard or soft. FUDFear, Uncertainty, and Doubt – negative sentiment spread to influence prices downward. Gas FeesThe cost paid to process transactions on networks like Ethereum. HalvingAn event that reduces the block reward by half, built into protocols like Bitcoin to control supply. Hardware WalletA physical device for storing private keys offline, such as Ledger or Trezor. HashA fixed-length string produced by a cryptographic function from input data, used to secure blocks. HODLA term meaning to hold onto assets long-term despite volatility (originated from a typo). Hot WalletAn online-connected wallet for convenient access, but more vulnerable to attacks. Initial Coin Offering (ICO)A fundraising method where new projects sell tokens to early investors. KYC (Know Your Customer)Verification process required by exchanges to confirm user identity. Layer 2Solutions built on top of base blockchains to improve scalability, like Lightning Network for Bitcoin. LiquidityThe ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price. Market Capitalization (Market Cap)The total value of a cryptocurrency's circulating supply (price multiplied by supply). Meme CoinCryptocurrencies inspired by internet memes, often driven by community hype. MetaverseVirtual shared spaces combining augmented and virtual reality, often integrated with blockchain. MiningThe process of validating transactions and adding blocks using computational power. Mnemonic Phrase (Seed Phrase)A sequence of words used to recover a wallet if access is lost. NFT (Non-Fungible Token)A unique digital asset representing ownership of items like art or collectibles. NodeA computer that participates in a blockchain network by maintaining a copy of the ledger. Private KeyA secret code that allows spending of cryptocurrency from a wallet. Proof of Stake (PoS)A consensus mechanism where validators are chosen based on staked coins. Proof of Work (PoW)A consensus mechanism requiring computational effort, used by Bitcoin. Public KeyA visible address derived from the private key, used to receive funds. Pump and DumpA scheme where prices are artificially inflated before insiders sell off. Rug PullA scam where developers abandon a project after raising funds, crashing the token value. SatoshiThe smallest unit of Bitcoin, named after its creator (1 BTC = 100 million satoshis). Satoshi NakamotoThe pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin. ScalabilityThe ability of a blockchain to handle increasing numbers of transactions efficiently. Smart ContractSelf-executing code on a blockchain that automatically enforces agreements. StablecoinA cryptocurrency pegged to a stable asset, like USDT or USDC, to minimize volatility. StakingLocking coins to support a Proof of Stake network and earn rewards. TokenA digital asset issued on an existing blockchain, often representing utility or ownership. Transaction FeeThe cost paid to network validators for processing a transfer. WalletSoftware or hardware that stores private and public keys for managing cryptocurrency. Web3The next evolution of the internet, emphasizing decentralization and user ownership. WhaleAn individual or entity holding large amounts of a cryptocurrency, capable of influencing markets. Yield FarmingProviding liquidity to DeFi protocols to earn rewards. Zero-Knowledge ProofA method allowing one party to prove knowledge without revealing the information itself. This covers the core 50 terms most frequently encountered by newcomers. Below are 50 additional important terms to round out your knowledge. 51. 51% Attack – When a group controls over half the network's mining power, potentially rewriting history.52. Atomic Swap – Direct peer-to-peer exchange across different blockchains.53. Bagholder – Someone holding a losing investment hoping for recovery.54. Bridge – Protocol connecting different blockchains for asset transfers.55. Burn – Permanently removing tokens from circulation.56. Circulating Supply – The amount of coins available in the market.57. DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) – Entity governed by smart contracts and token holders.58. DYOR (Do Your Own Research) – Advice to investigate before investing.59. EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) – Runtime environment for Ethereum smart contracts.60. FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) – Anxiety driving impulsive buys during rallies.61. Governance Token – Token granting voting rights in a protocol.62. Hard Cap – Maximum fundraising limit in a token sale.63. Immutable – Unable to be changed once recorded on the blockchain.64. Interoperability – Ability of different blockchains to communicate.65. Ledger – Record of all transactions on a blockchain.66. Lightning Network – Layer 2 solution for faster Bitcoin transactions.67. Liquidity Pool – Locked funds enabling trading on DEXs.68. Mainnet – The live, operational version of a blockchain.69. Multisig (Multi-Signature) – Wallet requiring multiple approvals for transactions.70. Oracle – Service providing external data to smart contracts.71. Paper Wallet – Physical printout of keys for offline storage.72. Protocol – Set of rules governing a blockchain network.73. Replay Attack – Reusing valid data maliciously on forked chains.74. Sharding – Dividing a blockchain to improve scalability.75. Sidechain – Separate blockchain linked to the main chain.76. Soft Fork – Backward-compatible blockchain update.77. Testnet – Experimental network for testing features.78. Total Supply – Maximum coins that will ever exist.79. Transaction ID (TXID) – Unique identifier for a blockchain transaction.80. TVL (Total Value Locked) – Amount of assets in DeFi protocols.81. Validator – Participant securing Proof of Stake networks.82. Vaporware – Announced project with no real development.83. Volume – Total amount traded in a period.84. Wrapped Token – Token representing another asset on a different chain.85. 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) – Extra security layer for accounts.86. Blockchain Explorer – Tool to view transactions and blocks.87. Cross-Chain – Interactions between different blockchains.88. Dust – Tiny amounts of cryptocurrency left over.89. Epoch – Time period in some consensus mechanisms.90. Flippening – Hypothetical event where Ethereum surpasses Bitcoin in market cap.91. Genesis Block – The very first block in a blockchain.92. Hash Rate – Measure of mining power on a network.93. Institutional Adoption – Large organizations entering crypto.94. Merkle Tree – Data structure verifying transactions efficiently.95. On-Chain – Transactions recorded directly on the blockchain.96. Off-Chain – Transactions or data handled outside the main blockchain.97. Permissionless – Open to anyone without approval.98. Rebase – Automatic supply adjustment in some tokens.99. Slippage – Difference between expected and executed trade price.100. UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) – Model used by Bitcoin for tracking balances. Why Understanding These Terms Matters Mastering this vocabulary does more than help you follow conversations. It empowers you to evaluate projects, spot potential risks, and navigate platforms confidently. Many beginners lose funds simply because they misunderstand basic concepts like private keys or phishing attempts. With these terms in your toolkit, you are ready to take practical steps. Explore our detailed tutorials on setting up a Phantom wallet for Solana or learn the fundamentals of secure storage in our best crypto exchanges guide. Crypto continues to mature in 2026, but the foundational terms remain largely the same. Bookmark this page and refer back as needed. Welcome to the space – informed beginners become the most successful long-term participants.
-
 Nefu
Nefu - 21 Dec 2025
- Getting started
How to Buy Crypto with Credit Card or PayPal : Fast and Safe Options for Beginners
Introduction: Buying Crypto with Credit Card or PayPal in 2026 Many beginners want the fastest and most familiar way to enter cryptocurrency: using a credit card or PayPal. These methods offer instant purchases without waiting for bank transfers, making them ideal for those ready to buy Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other assets right away. Searches like "buy crypto with credit card," "buy bitcoin with paypal," and "best way to buy crypto instantly 2026" continue to drive significant traffic because convenience matters. In 2026, more regulated platforms support these options while maintaining strong security standards. This guide focuses on safe, reputable ways to buy crypto using credit cards or PayPal. We compare top platforms, explain the process step by step, highlight fees and limits, and share essential safety tips. Whether you are making your first purchase or adding to your portfolio, these methods can work well when used wisely. For long-term security, plan to move funds to a personal wallet covered in our best crypto wallets for beginners. Pros and Cons of Using Credit Card or PayPal AdvantagesInstant funding – no multi-day bank waits. Familiar payment flow similar to online shopping. Buyer protection features on many cards and PayPal. Widely accepted on beginner-friendly platforms.DisadvantagesHigher fees compared to bank transfers (typically 2-4%). Some platforms treat card purchases as cash advances (extra issuer fees). Lower limits for new accounts. Not all decentralized exchanges support fiat on-ramps.Understanding these trade-offs helps you decide when this method fits your needs. Top Platforms That Accept Credit Card or PayPal in 2026 Several trusted platforms make instant purchases straightforward. 1. Coinbase One of the most beginner-friendly exchanges with strong regulation.Accepts Visa and Mastercard debit/credit cards. PayPal available for withdrawals and limited purchases in supported regions. Instant buys up to account limits. Clear fee structure displayed before confirmation.2. Binance Global leader with competitive pricing.Credit/debit card purchases via integrated third-party providers. PayPal supported in select countries. Wide range of cryptocurrencies available immediately.3. Kraken Known for security and transparency.Direct credit/debit card purchases. PayPal integration for certain regions. Lower fees than many competitors for card transactions.4. Crypto.com Popular for its Visa card rewards program.Accepts credit/debit cards and PayPal in many jurisdictions. Instant deposits to buy crypto or load their debit card.5. eToro Social trading platform with crypto offerings.Credit card and PayPal deposits supported. User-friendly interface for beginners. Copy-trading features to follow experienced investors.6. MoonPay (Third-Party On-Ramp) Widget used by many wallets and dApps.Supports credit cards and PayPal globally. Sends crypto directly to your personal wallet address. Higher fees but maximum convenience.Step-by-Step: How to Buy Crypto with Credit Card The process is similar across platforms. Here is a general walkthrough using Coinbase as an example.Create and Verify AccountSign up with email and complete KYC (identity verification) – required for fiat purchases.Add Payment MethodLink your credit card. Some platforms require 3D Secure verification.Choose CryptocurrencySelect Bitcoin, Ethereum, or another asset.Enter AmountInput dollar value or crypto quantity. Review fees shown upfront.Confirm PurchaseComplete card authentication if prompted.Receive CryptoAssets appear in your exchange wallet instantly or within minutes.Transfer to Personal WalletFor security, move to a non-custodial wallet soon after.Follow similar steps on other platforms. Always start with a small test transaction. Step-by-Step: How to Buy Crypto with PayPal PayPal availability varies by country, but the flow is straightforward where supported.Link PayPal AccountConnect during deposit setup.Select PayPal as Funding SourceChoose during purchase or deposit.Authorize PaymentLog in to PayPal and confirm.Complete TransactionFunds convert to crypto instantly.Note: PayPal sometimes restricts crypto-related transactions, so verify current policy. Fees and Limits to UnderstandPlatform Card Fee Range PayPal Fee Typical New User LimitCoinbase 3.99% Varies $1,000–$5,000 weeklyBinance 1.8–3.5% Varies Varies by verificationKraken 3.75% + $0.26 N/A Tier-basedCrypto.com 2.99% Supported ProgressiveMoonPay 4.5–5% 4–5% Higher limitsFees decrease with higher verification levels or VIP status. Compare before committing. Safety Tips for Card and PayPal PurchasesUse platforms with strong regulation and insurance. Enable two-factor authentication. Verify HTTPS and official app sources. Monitor card statements for unauthorized charges. Avoid public Wi-Fi for transactions. Consider cards with rewards or fraud protection.Never share card details or PayPal credentials outside official sites. Alternatives If Card or PayPal Are Restricted Some regions face limitations. Alternatives include:Bank transfers (slower but cheaper). Apple Pay/Google Pay where supported. Peer-to-peer platforms with buyer protection.After Purchase: Next StepsSecure Your AssetsTransfer to a personal wallet immediately for larger amounts.Track Your InvestmentUse portfolio apps or spreadsheets.Plan Your StrategyConsider dollar-cost averaging to reduce timing stress – see our crypto psychology guide.Stay InformedFollow reputable sources and avoid hype-driven decisions.Conclusion: Start Your Journey Conveniently and Safely Buying crypto with a credit card or PayPal offers one of the quickest paths for beginners in 2026. While fees are higher than bank transfers, the speed and familiarity make it worthwhile for initial purchases or opportunistic buys. Choose established platforms, understand costs, and prioritize security throughout the process. Combine convenience with discipline for the best outcomes. Ready for more? Compare full features in our best crypto exchanges review or follow detailed buying steps in our main how to buy crypto guide. Your informed entry into cryptocurrency starts here.

-
 Nefu
Nefu - 21 Dec 2025
- Security privacy
How to Revoke Token Allowances on Ethereum, Arbitrum, & BSC
#Cut the Cord: Revoking Unlimited Token Allowances on EVM Chains When participating in airdrop farming across EVM-compatible networks (like Ethereum, Arbitrum, BNB Chain, Polygon, etc.), you constantly interact with new smart contracts. Every time you swap, stake, or provide liquidity, your wallet is prompted to grant a Token Allowance (also known as a token approval). Understanding and managing these allowances is the single most important security practice on EVM. 1. What is a Token Allowance? A Token Allowance is the permission you grant a smart contract to move a specific amount of one of your tokens on your behalf.The Approval: You sign a transaction authorizing a dApp's contract (the Spender) to transfer your tokens (the Owner) up to a specified amount (the Allowance). The Risk: Most dApps default to asking for an "Unlimited" allowance. This is convenient because you only pay the gas fee once, but it means that contract can technically drain your entire balance of that token forever.The Danger of Unlimited Allowance If a protocol you granted unlimited access to is later hacked, exploited, or turned malicious, the attacker can use the existing permission to call the contract and drain your wallet of the approved tokens without any further action or signature from you. Disconnecting your MetaMask or Trust Wallet DOES NOT remove this permission! The permission is written to the blockchain.2. The Solution: Multi-Chain Revocation with Revoke.cash To maintain a secure "Wallet Hygiene," you must periodically check your allowances and revoke any that are unnecessary. The most widely recognized and easiest tool for this across all major EVM chains is Revoke.cash. Step-by-Step Revocation Guide: Follow these steps using your Burner Wallet (or any wallet you use for farming) to manage your allowances. 1. Access the Revoke Tool:Navigate to the official Revoke.cash website. Always verify the URL is correct to prevent phishing.2. Connect Wallet and Select Network:Click 'Connect Wallet' (e.g., MetaMask, WalletConnect). IMPORTANT: Use the network selection menu (usually in the top right) to choose the blockchain you want to audit (e.g., Ethereum, Arbitrum, BNB Chain, Polygon). You must check each chain separately!3. Review Active Allowances:The tool will scan the selected network and display a list of all your active token allowances. The list shows: The Token (e.g., ETH, USDC, DAI). The Spender (the contract that has permission). The Allowance Amount (often displayed as "Unlimited" or a very large number).4. Identify and Prioritize Revocations:Priority 1: Revoke unlimited allowances for high-value assets (USDC, USDT, ETH) on platforms you no longer use. Priority 2: Revoke any approvals for tokens from projects you suspect might be scams or have minimal TVL (Total Value Locked).5. Execute the Revocation Transaction:Click the 'Revoke' button next to the specific allowance you want to cut off. Your wallet (e.g., MetaMask) will prompt you to sign a transaction. This transaction calls the original token contract and sets the allowance to zero (0). Gas Fee: Note that revoking an allowance is a transaction written to the blockchain, and therefore costs a small amount of the native currency (e.g., ETH on Ethereum, BNB on BSC, or ARB on Arbitrum) to pay the gas fee.6. Confirmation:Once the transaction confirms on the blockchain, the contract's permission is permanently removed.Pro-Tip: Setting Custom Allowances To prevent the need for constant revocation, many wallets (like MetaMask) allow you to edit the spending limit when prompted for an approval:When the approval pop-up appears, look for the 'Edit Permission' or 'Custom Spend Limit' option. Instead of leaving it as "Unlimited," enter a specific amount slightly higher than your planned transaction (e.g., if you plan to swap $100 USDC, set the allowance to $110 USDC).This limits the potential damage of an exploit, but you will have to re-approve the contract when you exceed that custom limit.
